
Jousting
Jousting is based on the military use of the lance by heavy cavalry. It transformed into a specialised sport during the Late Middle Ages, and remained popular with the nobility both in England and Germany throughout the whole of the 16th century (while in France, it was discontinued after the death of King Henry II in an accident in 1559). In England, jousting was the highlight of the Accession Day tilts of Elizabeth I and James I, and also was part of the festivities at the marriage of Charles I.
King Arthur
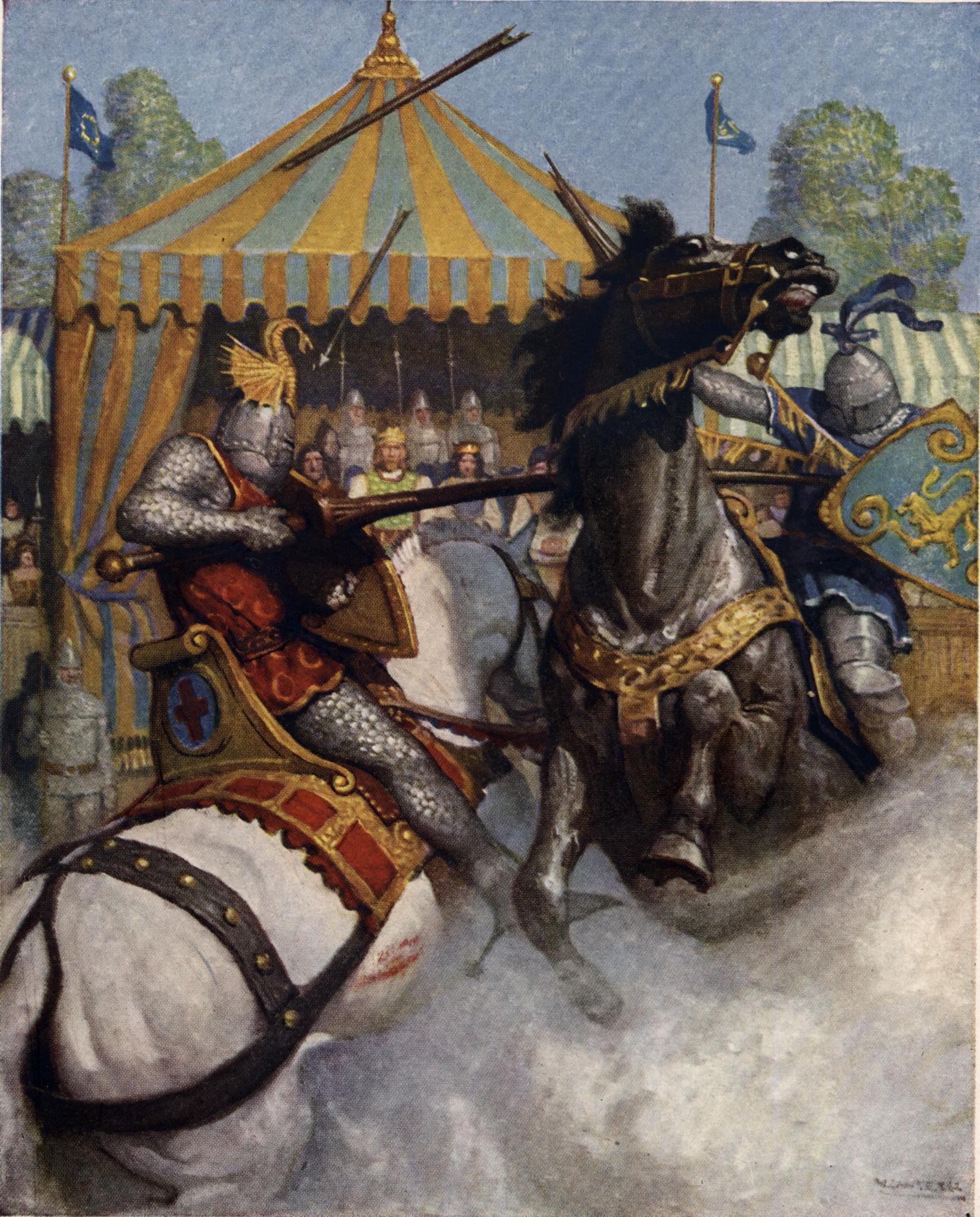
NOW, said the king, I am sure at this quest of the Sangreal shall all ye of the Table Round depart, and never shall I see you again whole together; therefore I will see you all whole together in the meadow of Camelot to joust and to tourney, that after your death men may speak of it that such good knights were wholly together such a day. As unto that counsel and at the king’s request they accorded all, and took on their harness that longed unto jousting. But all this moving of the king was for this intent, for to see Galahad proved; for the king deemed he should not lightly come again unto the court after his departing. So were they assembled in the meadow both more and less. Then Sir Galahad, by the prayer of the king and the queen, did upon him a noble jesseraunce, and also he did on his helm, but shield would he take none for no prayer of the king. And then Sir Gawaine and other knights prayed him to take a spear. Right so he did; and the queen was in a tower with all her ladies, for to behold that tournament. Then Sir Galahad dressed him in middes of the meadow, and began to break spears marvelously, that all men had wonder of him; for he there surmounted all other knights, for within a while he had defouled many good knights of the Table Round save twain, that was Sir Launcelot and Sir Percivale.

